Acronyms:
Files and Directories
Useful Views/Tables
Useful Parameters
Processes
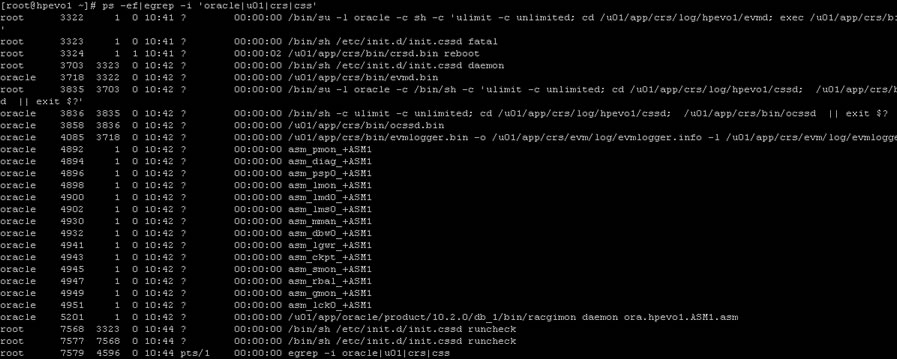
General Administration
CRS Administration
Voting Disk
Acronyms
| ||
| GCS | Global Cache Services | in memory database containing current locks and awaiting locks, also known as PCM |
| GES | Global Enqueue Services | coordinates the requests of all global enqueues uses the GCS, also known as non-PCM |
| GRD | Global Resource Directory | all resources available to the cluster (formed and managed by GCS and GES), see GRDfor more details |
| GRM | Global Resource Manager | helps to coordinate and communicate the locks requests between Oracle processes |
| GSD | Global Services Daemon | runs on each node with one GSD process per node. The GSD coordinates with the cluster manager to receive requests from clients such as the DBCA, EM, and the SRVCTL utility to execute administrative job tasks such as instance startup or shutdown. The GSD is not an Oracle instance background process and is therefore not started with the Oracle instance |
| PCM (IDLM) | Parallel Cache Management | formly know as (integrated) Distributed Lock Manager, its another name for GCS |
| Resource | n/a | it is a identifiable entity it basically has a name or a reference, it can be a area in memory, a disk file or an abstract entity |
| Resource (Global) | n/a | a resource that can be accessed by all the nodes within the cluster examples would be the following
|
| LVB | Lock Value Block | contains a small amount of data regarding the lock |
| TRFC | Traffic Controller | controls the DLM traffic between instances (messaging tickets) |
Files and Directories
| |
| $ORA_CRS_HOME/cdata/<cluster_name> | OCR backups (default location) |
| $ORA_HOME/log/<hostname>/client/ocrconfig_<pid>.log | OCR command log file |
| $ORA_CRS_HOME/crs/log | contains trace files for the CRS resources |
| $ORA_CRS_HOME/crs/init | contains trace files for the CRS daemon during startup, a good place to start |
| $ORA_CRS_HOME/css/log | contains cluster reconfigurations, missed check-ins, connects and disconnects from the client CSS listener. Look here to obtain when reboots occur |
| $ORA_CRS_HOME/css/init | contains core dumps from the cluster synchronization service daemon (OCSd) |
| $ORA_CRS_HOME/evm/log | logfiles for the event volume manager and eventlogger daemon |
| $ORA_CRS_HOME/evm/init | pid and lock files for EVM |
| $ORA_CRS_HOME/srvm/log | logfiles for Oracle Cluster Registry (OCR) |
| $ORA_CRS_HOME/log | log fles for Oracle clusterware which contains diagnostic messages at the Oracle cluster level |
GCS and Cache Fusion Diagnostics
| |
| v$cache | contains information about every cached block in the buffer cache |
| v$cache_transfer | contains information from the block headers in SGA that have been pinged at least once |
| v$instance_cache_transfer | contains information about the transfer of cache blocks through the interconnect |
| v$cr_block_server | contains statistics about CR block transfer across the instances |
| v$current_block_server | contains statistics about current block transfer across the instances |
| v$gc_element | contains one-to-one information for each global cache resource used by the buffer cache |
GES diagnostics
| |
| v$lock | contains information about locks held within a database and outstanding requests for locks and latches |
| v$ges_blocking_enqueue | contains information about locks that are being blocked or blocking others and locks that are known to the lock manager |
| v$enqueue_statistics | contains details about enqueue statistics in the instance |
| v$resource_limits | display enqueue statistics |
| v$locked_object | contains information about DML locks acquired by different transactions in databases with their mode held |
| v$ges_statistics | contains miscellaneous statistics for GES |
| v$ges_enqueue | contains information about all locks known to the lock manager |
| v$ges_convert_local | contains information about all local GES operations |
| v$ges_convert_remote | contains information about all remote GES operations |
| v$ges_resource | contains information about all resources known to the lock manager |
| v$ges_misc | contains information about messaging traffic information |
| v$ges_traffic_controller | contains information about the message ticket usage |
Dynamic Resource Remastering
| |
| v$hvmaster_info | contains information about current and previous master instances of GES resources in relation to hash value ID of resource |
| v$gcshvmaster_info | the same as above but globally |
| v$gcspfmaster_info | conatins information about current and previous masters about GCS resources belonging to files mapped to a particular master, including the number of times the resource has remastered |
Cluster Interconnect
| |
| v$cluster_interconnects | contains information about interconnects that are being used for cluster communication |
| v$configured_interconnects | same as above but also contains interconnects that AC is aware off that are not being used |
Miscellanous
| |
| v$service | services running on an instance |
| x$kjmsdp | display LMS daemon statistics |
| x$kjmddp | display LMD daemon statistics |
Parameters
| |
| cluster_interconnects | specify a specific IP address to use for the inetrconnect |
| _gcs_fast_config | enables fast reconfiguration for gcs locks (true|false) |
| _lm_master_weight | controls which instance will hold or (re)master more resources than others |
| _gcs_resources | controls the number of resources an instance will master at a time |
| _lm_tickets | controls the number of message tickets |
| _lm_ticket_active_sendback | controls the number of message tickets (aggressive messaging) |
| _db_block_max_cr_dba | limits the number of CR copies per DBA on the buffer cache (see grd) |
| _fairness_threshold | used when too many CR requested arrive for a particular buffer and the block becomes disowned (see grd) |
| _gc_affinity_time | specifies interval minutes for reamstering |
| _gc_affinity_limit | defines the number of times a instance access the resource before remastering |
| _gc_affinity_minimum | defines the minimum number of times a instance access the resource before remastering |
| _lm_file_affinity | disables dynamic remastering for the objects belonging to those files |
| _lm_dynamic_remastering | enable or disable remastering |
| _gc_defer_time | define the time by which an instance deferred downgrading a lock (see Cache Fusion) |
| _lgwr_async_broadcast | change the SCN boardcast method (see troubleshooting) |

Oracle RAC Daemons and Processes
| ||
| OPROCd | Process Monitor | provides basic cluster integrity services |
| EVMd | Event Management | spawns a child process event logger and generates callouts |
| OCSSd | Cluster Synchronization Services | basic node membership, group services, basic locking |
| CRSd | Cluster Ready Services | resource monitoring, failover and node recovery |
LMSn
| Lock Manager Server process - GCS | this is the cache fusion part, it handles the consistent copies of blocks that are tranferred between instances. It receives requests from LMD to perform lock requests. I rools back any uncommitted transactions. There can be upto ten LMS processes running and can be started dynamically if demand requires it. they manage lock manager service requests for GCS resources and send them to a service queue to be handled by the LMSn process. It also handles global deadlock detection and monitors for lock conversion timeouts. |
LMON
| Lock Monitor Process - GES | this process manages the GES, it maintains consistency of GCS memory in case of process death. It is also responsible for cluster reconfiguration and locks reconfiguration (node joining or leaving), it checks for instance deaths and listens for local messaging. A detailed log file is created that tracks any reconfigurations that have happened. |
LMD
| Lock Manager Daemon - GES | this manages the enqueue manager service requests for the GCS. It also handles deadlock detention and remote resource requests from other instances. |
LCK0
| Lock Process - GES | manages instance resource requests and cross-instance call operations for shared resources. It builds a list of invalid lock elements and validates lock elements during recovery. |
DIAG
| Diagnostic Daemon | This is a lightweight process, it uses the DIAG framework to monitor the healt of the cluster. It captures information for later diagnosis in the event of failures. It will perform any neccessary recovery if an operational hang is detected. |
Managing the Cluster
| |
| starting | /etc/init.d/init.crs start crsctl start crs |
| stopping | /etc/init.d/init.crs stop crsctl stop crs |
| enable/disable at boot time | /etc/init.d/init.crs enable /etc/init.d/init.crs disable crsctl enable crs crsctl disable crs |
Managing the database configuration with SRVCTL
| |
| start all instances | srvctl start database -d <database> -o <option> Note: starts listeners if not already running, you can use the -o option to specify startup/shutdown options force open mount nomount |
| stop all instances | srvctl stop database -d <database> -o <option> Note: the listeners are not stopped, you can use the -o option to specify startup/shutdown options immediate abort normal transactional |
| start/stop particular instance | srvctl [start|stop] database -d <database> -i <instance>,<instance> |
| display the registered databases | srvctl config database |
| status | srvctl status database -d <database> srvctl status instance -d <database> -i <instance>,<instance> srvctl status service -d <database> srvctl status nodeapps -n <node> srvctl status asm -n <node> |
| stopping/starting | srvctl stop database -d <database> srvctl stop instance -d <database> -i <instance>,<instance> srvctl stop service -d <database> -s <service>,<service> -i <instance>,<instance> srvctl stop nodeapps -n <node> srvctl stop asm -n <node> srvctl start database -d <database> srvctl start instance -d <database> -i <instance>,<instance> srvctl start service -d <database> -s <service>,<service> -i <instance>,<instance> srvctl start nodeapps -n <node> srvctl start asm -n <node> |
| adding/removing | srvctl add database -d <database> -o <oracle_home> srvctl add instance -d <database> -i <instance> -n <node> srvctl add service -d <database> -s <service> -r <preferred_list> srvctl add nodeapps -n <node> -o <oracle_home> -A <name|ip>/network srvctl add asm -n <node> -i <asm_instance> -o <oracle_home> srvctl remove database -d <database> -o <oracle_home> srvctl remove instance -d <database> -i <instance> -n <node> srvctl remove service -d <database> -s <service> -r <preferred_list> srvctl remove nodeapps -n <node> -o <oracle_home> -A <name|ip>/network srvctl asm remove -n <node> |
OCR utilities
| |
| log file | $ORA_HOME/log/<hostname>/client/ocrconfig_<pid>.log |
| checking | ocrcheck Note: will return the OCR version, total space allocated, space used, free space, location of each device and the result of the integrity check |
| dump contents | ocrdump -backupfile <file> Note: by default it dumps the contents into a file named OCRDUMP in the current directory |
| export/import | ocrconfig -export <file> ocrconfig -restore <file> |
| backup/restore | # show backups ocrconfig -showbackup # to change the location of the backup, you can even specify a ASM disk ocrconfig -backuploc <path|+asm> # perform a backup, will use the location specified by the -backuploc location ocrconfig -manualbackup # perform a restore ocrconfig -restore <file> # delete a backup orcconfig -delete <file> Note: there are many more option so see the ocrconfig man page |
| add/remove/replace | ## add/relocate the ocrmirror file to the specified location ocrconfig -replace ocrmirror '/ocfs2/ocr2.dbf' ## relocate an existing OCR file ocrconfig -replace ocr '/ocfs1/ocr_new.dbf' ## remove the OCR or OCRMirror file ocrconfig -replace ocr ocrconfig -replace ocrmirror |
CRS Administration
| |
| starting | ## Starting CRS using Oracle 10g R1 not possible ## Starting CRS using Oracle 10g R2 $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crsctl start crs |
| stopping | ## Stopping CRS using Oracle 10g R1 srvctl stop database -d <database> srvctl stop asm -n <node> srvctl stop nodeapps -n <node> /etc/init.d/init.crs stop ## Stopping CRS using Oracle 10g R2 $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crsctl stop crs |
| disabling/enabling | ## use to stop CRS restarting after a reboot ## Oracle 10g R1 /etc/init.d/init.crs [disable|enable] ## Oracle 10g R2 $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crsctl [disable|enable] crs |
| checking | $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crsctl check crs $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crsctl check evmd $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crsctl check cssd $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crsctl check crsd $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crsctl check install -wait 600 |
Resource Applications (CRS Utilities)
| |
| status | $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crs_stat |
| create profile | $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crs_profile |
| register/unregister application | $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crs_register $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crs_unregister |
| Start/Stop an application | $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crs_start $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crs_stop |
| Resource permissions | $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crs_getparam $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crs_setparam |
| Relocate a resource | $ORA_CRS_HOME/bin/crs_relocate |
Nodes
| |
| member number/name | olsnodes -n |
| local node name | olsnodes -l |
| activates logging | olsnodes -g |
Oracle Interfaces
| |
| display | oifcfg getif |
| delete | oicfg delig -global |
| set | oicfg setif -global <interface name>/<subnet>:public oicfg setif -global <interface name>/<subnet>:cluster_interconnect |
Global Services Daemon Control
| |
| starting | gsdctl start |
| stopping | gsdctl stop |
| status | gsdctl status |
Cluster Configuration (clscfg is used during installation)
| |
| create a new configuration | clscfg -install |
| upgrade or downgrade and existing configuration | clscfg -upgrade clscfg -downgrade |
| add or delete a node from the configuration | clscfg -add clscfg -delete |
| create a special single-node configuration for ASM | clscfg -local |
| brief listing of terminology used in the other nodes | clscfg -concepts |
| used for tracing | clscfg -trace |
| help | clscfg -h |
Cluster Name Check
| |
| print cluster name | cemulto -n Note: in Oracle 9i the ulity was called "cemutls" |
| print the clusterware version | cemulto -w Note: in Oracle 9i the ulity was called "cemutls" |
Node Scripts
| |
| Add Node | addnode.sh Note: see adding and deleting nodes |
| Delete Node | deletenode.sh Note: see adding and deleting nodes |
Enqueues
| |
| displaying statistics | SQL> column current_utilization heading current SQL> column max_utilization heading max_usage SQL> column initial_allocation heading initial SQL> column resource_limit format a23; SQL> select * from v$resource_limit; |
Messaging (tickets)
| |
| ticket usage | select local_nid local, remote_nid remote, tckt_avail avail, tckt_limit limit, snd_q_len send_queue, tckt_wait waiting from v$ges_traffic_controller; |
| dump ticket information | SQL> oradebug setmypid SQL> oradebug unlimit SQL> oradebug lkdebug -t |
Lighwork Rule and Fairness Threshold
| |
| downconvert | select cr_requests, light_works, data_requests, fairness_down_converts from v$cr_block_server; Note: lower the _fairness_threshold if the ratio goes above 40%, set to 0 if the instance is a query only instance. |
Remastering
| |
| force dynamic remastering (DRM) | ## Obtain the OBJECT_ID form the below table SQL> select * from v$gcspfmaster_info; ## Determine who masters it SQL> oradebug setmypid SQL> oradebug lkdebug -a <OBJECT_ID> ## Now remaster the resource SQL> oradebug setmypid SQL> oradebug lkdebug -m pkey <OBJECT_ID> |
GRD, SRVCTL, GSD and SRVCONFIG Tracing
| |
| Enable tracing | $ export SRVM_TRACE=true |
| Disable tracing | $ export SRVM_TRACE="" |
| adding | crsctl add css votedisk <file> |
| deleting | crsctl delete css votedisk <file> |
| querying | crsctl query css votedisk |
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.